
A brand new examine signifies {that a} blended microplastic mix could also be considerably extra poisonous than a single polymer on a key marine food-web species.
As a result of big selection of how wherein microplastics can enter the pure atmosphere, microplastic air pollution is extraordinarily various when it comes to materials make-up, measurement, form, chemical composition, color and state of degradation. This range causes challenges not just for marine life but in addition for scientific research.
To assist tackle these challenges in monitoring and experimentation, facilitate methodological harmonisation and promote comparative analyses between research, a crew of scientists from the UK and Norway tailored present experimental strategies to conduct full and partial life-cycle, mixed-microplastic toxicity assessments on the grownup and juvenile levels of the ecologically-important copepod Acartia tonsa.
Marine copepods play a important position within the international ocean, supporting meals webs, and contributing to fisheries productiveness, nutrient flux and carbon sequestration. Given their ecological significance, international distribution and excessive abundance, sensitivity to environmental stressors and ease of culturing, copepods are really useful as useful mannequin organisms for toxicological testing.
Prior research have noticed 0.006-0.032 millimetres (mm, 6–31μm) microplastics will be readily ingested by A. tonsa whereas 0.00004-0.0038mm (0.4–3.8μm) microplastics can adhere to the outside and appendages of sure copepod species.
Experiment and findings
The purpose of the experiments was to disclose whether or not acute and power publicity to a mix of microplastics pose deadly or sublethal dangers to a globally-relevant marine species. With endpoints corresponding to grownup survival, algal ingestion charges, egg manufacturing, egg measurement, larval growth ratio and juvenile survival, this analysis would help the event of threat assessments and air pollution thresholds.
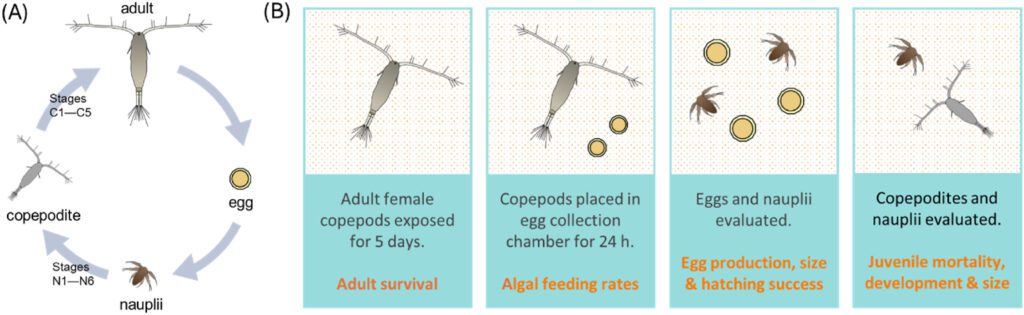
The methodology includes a 72 hour acute toxicity check with grownup A. tonsa and a 5 day publicity utilizing grownup females to find out results on egg manufacturing and offspring growth.
The microplastics constituting the tri-polymer mix had been chemically characterised to disclose the chemical compounds current within the polymers, which may doubtlessly contribute to noticed toxicity. The mix comprised cryoground polyethylene (a post-consumer blended polymer), polypropylene (used for packaging, textiles and automotive components) and nylon particles at concentrations ranging 0-1 milligrams (mg) per litre, and had been chosen as these are generally discovered inside environmental water samples.
Mortality, egg measurement and larval growth ratio proved to be essentially the most delicate endpoints when A. tonsa was uncovered to the fully-characterised tri-polymer microplastic mix.
The experiment resulted in a 50% mortality price when people had been uncovered to a tri-polymer focus of 0.182mg per litre, comparable with excessive environmental concentrations present in microplastic hotspots, and a 100% mortality price at concentrations between 0.4 and 0.6mg per litre.
On condition that mortality is an unusual endpoint in microplastic research, with microplastic results sometimes being related to sublethal hurt, this examine means that the tri-polymer mix is considerably extra poisonous than a single polymer publicity.
Dr Zara Botterell, lead creator and PhD Fellow at Plymouth Marine Laboratory and the College of Exeter, mentioned:
“This examine supplies necessary knowledge for subsequent threat evaluations and the willpower of toxicity thresholds. For grownup A. tonsa there was a 50% mortality price at a focus of 0.182mg per litre and general, grownup survival was recognized as a considerably delicate endpoint”.
The power publicity examine confirmed restricted proof of sub-lethal well being results on juvenile life levels. Moreover, chemical evaluation of the tri-polymer mix revealed a number of leachate compounds, nevertheless, the variety of chemical compounds with anticipated hazardous properties was low in comparison with client plastics and signifies a restricted variety of chemical compounds with potential for contributing to toxicity.
Dr Botterell added: “Regardless of measuring many endpoints inside the partial life-cycle check, there was restricted proof of sub-lethal results on the juvenile life levels utilizing environmentally related concentrations. Nevertheless, we offer a number of suggestions and recommendations which can support and enhance future toxicity check protocols, together with elevated replication (particular person and therapy numbers) and software program automation”.

A brand new examine signifies {that a} blended microplastic mix could also be considerably extra poisonous than a single polymer on a key marine food-web species.
As a result of big selection of how wherein microplastics can enter the pure atmosphere, microplastic air pollution is extraordinarily various when it comes to materials make-up, measurement, form, chemical composition, color and state of degradation. This range causes challenges not just for marine life but in addition for scientific research.
To assist tackle these challenges in monitoring and experimentation, facilitate methodological harmonisation and promote comparative analyses between research, a crew of scientists from the UK and Norway tailored present experimental strategies to conduct full and partial life-cycle, mixed-microplastic toxicity assessments on the grownup and juvenile levels of the ecologically-important copepod Acartia tonsa.
Marine copepods play a important position within the international ocean, supporting meals webs, and contributing to fisheries productiveness, nutrient flux and carbon sequestration. Given their ecological significance, international distribution and excessive abundance, sensitivity to environmental stressors and ease of culturing, copepods are really useful as useful mannequin organisms for toxicological testing.
Prior research have noticed 0.006-0.032 millimetres (mm, 6–31μm) microplastics will be readily ingested by A. tonsa whereas 0.00004-0.0038mm (0.4–3.8μm) microplastics can adhere to the outside and appendages of sure copepod species.
Experiment and findings
The purpose of the experiments was to disclose whether or not acute and power publicity to a mix of microplastics pose deadly or sublethal dangers to a globally-relevant marine species. With endpoints corresponding to grownup survival, algal ingestion charges, egg manufacturing, egg measurement, larval growth ratio and juvenile survival, this analysis would help the event of threat assessments and air pollution thresholds.

The methodology includes a 72 hour acute toxicity check with grownup A. tonsa and a 5 day publicity utilizing grownup females to find out results on egg manufacturing and offspring growth.
The microplastics constituting the tri-polymer mix had been chemically characterised to disclose the chemical compounds current within the polymers, which may doubtlessly contribute to noticed toxicity. The mix comprised cryoground polyethylene (a post-consumer blended polymer), polypropylene (used for packaging, textiles and automotive components) and nylon particles at concentrations ranging 0-1 milligrams (mg) per litre, and had been chosen as these are generally discovered inside environmental water samples.
Mortality, egg measurement and larval growth ratio proved to be essentially the most delicate endpoints when A. tonsa was uncovered to the fully-characterised tri-polymer microplastic mix.
The experiment resulted in a 50% mortality price when people had been uncovered to a tri-polymer focus of 0.182mg per litre, comparable with excessive environmental concentrations present in microplastic hotspots, and a 100% mortality price at concentrations between 0.4 and 0.6mg per litre.
On condition that mortality is an unusual endpoint in microplastic research, with microplastic results sometimes being related to sublethal hurt, this examine means that the tri-polymer mix is considerably extra poisonous than a single polymer publicity.
Dr Zara Botterell, lead creator and PhD Fellow at Plymouth Marine Laboratory and the College of Exeter, mentioned:
“This examine supplies necessary knowledge for subsequent threat evaluations and the willpower of toxicity thresholds. For grownup A. tonsa there was a 50% mortality price at a focus of 0.182mg per litre and general, grownup survival was recognized as a considerably delicate endpoint”.
The power publicity examine confirmed restricted proof of sub-lethal well being results on juvenile life levels. Moreover, chemical evaluation of the tri-polymer mix revealed a number of leachate compounds, nevertheless, the variety of chemical compounds with anticipated hazardous properties was low in comparison with client plastics and signifies a restricted variety of chemical compounds with potential for contributing to toxicity.
Dr Botterell added: “Regardless of measuring many endpoints inside the partial life-cycle check, there was restricted proof of sub-lethal results on the juvenile life levels utilizing environmentally related concentrations. Nevertheless, we offer a number of suggestions and recommendations which can support and enhance future toxicity check protocols, together with elevated replication (particular person and therapy numbers) and software program automation”.














