Lithium-ion batteries are a useful know-how used to transition us away from fossil fuels by electrifying transportation and supporting renewable power sources. The batteries comprise minerals that may be recovered to be used in future batteries, together with lithium, cobalt, nickel, copper, aluminum, and graphite.
Sourcing supplies from recycling is extra sustainable than mining virgin supplies, and in some instances, it’s the one viable home possibility for the USA (US) the place most battery supplies or the batteries themselves are imported. Nevertheless, minerals aren’t all the time recovered at excessive charges throughout recycling, both as a result of the most effective accessible know-how isn’t used or as a result of low or unstable mineral costs make the restoration of some minerals uneconomical for recyclers. Which means these minerals are successfully misplaced from the availability chain after they in any other case would have been a invaluable useful resource.
However, there’s a resolution. Setting required mineral restoration charges ensures {that a} excessive share of minerals from retired batteries goes again into the US economic system and reduces mining wants. When partnered with a coverage that requires producers to recycle batteries within the US, recycling firms aren’t topic to the volatility of worldwide mineral costs.
With out any such coverage, mineral restoration charges may undergo throughout worth drops, due to this fact forgoing a possibility to develop a lower-impact home provide chain of battery supplies to assist maintain continued progress within the US battery manufacturing sector. Take, for instance, the aluminum scrap market, which is frequently impacted by fluctuating costs that lead to decrease recycling charges. Aluminum recycling is at the moment at a 30-year low, right down to solely a 43% recycling charge. Whereas aluminum operates in a different way than the retired battery market (black mass), the foundation of the trigger is identical – market volatility hurts restoration charges.
The European Union is beginning to deal with this difficulty. In 2023 they created a complete battery coverage that features obligatory mineral restoration charges. They simply launched tips for calculating and verifying recycling effectivity and restoration of supplies from waste batteries. Because the European Union is the chief for any such coverage, the USA can be taught from their strategy and equally guarantee:
- Decreased quantity of mining wanted for car electrification;
- excessive mineral restoration and mineral manufacturing in the USA to maximise advantages; and
- US recycling firms are supported throughout occasions of fluctuating mineral costs, and know-how and home mineral manufacturing doesn’t lag behind different areas.
What are the European Union mineral restoration charge necessities?
A restoration charge is the quantity of a mineral that’s recovered in a usable kind in comparison with the overall quantity within the waste batteries that had been recycled. Whereas batteries comprise a handful of minerals, the European Union has solely set necessities for lithium, nickel, cobalt, and copper due to the rising demand for clear know-how and the reliance on imports of those minerals.
The necessities improve over time; the mineral restoration necessities are 90% for cobalt, copper, and nickel and 50% for lithium by 2028. They improve to 95% for cobalt, copper, and nickel and 80% for lithium by 2032. Lithium restoration necessities are decrease than the opposite minerals as a result of not all amenities and processes get well the mineral at present, due to this fact these necessities might require ramping up that functionality.
Importantly, these necessities don’t exceed technological feasibility. For instance, researchers just lately analyzed knowledge from Redwood Supplies, a number one battery recycler within the US, and located they will get well properly above these ranges of their latest Nature article.
How are mineral restoration charges calculated?
The best recycling insurance policies comprise restoration charge necessities however together with them means every facility must have a typical means of calculating to make sure compliance. The European Fee just lately resolved this downside by releasing steerage on how every facility ought to calculate and confirm the restoration charges. The USA is exploring how to make sure mineral restoration by means of restoration charges, and this strategy may very well be utilized to the recycling coverage beneath improvement.
The restoration charges of every mineral are calculated yearly and take into account the minerals contained within the battery or black mass going into every step of the recycling course of, after which the output of supplies that may then be used to fabricate new merchandise.
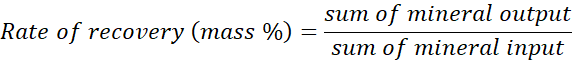
Discovering the mineral output is simple and is one thing recyclers already do since they want to resell the minerals they get well. Figuring out the mineral enter, nevertheless, will not be so simple as it appears however can be essential. It is because there may be an array of battery chemistries and the batteries aren’t all the time labeled, so recyclers might not know the precise make-up of the batch they’re processing. Fortunately, that is one thing that may be addressed with required labels within the battery recycling coverage itself.
The rules advocate conducting a sorting evaluation of the enter supplies by steady or consultant sampling. The recyclers can do that by one of many following:
- labels or a web based database (if accessible) to find out battery chemistry;
- sampling and analyzing the composition of batteries or black mass coming into the waste stream; or
- decide the composition of all of the output minerals plus emissions and waste ensuing from remedy.
How would restoration charges affect US recycled content material?
Minimal mineral restoration charges will assist make sure that future mining is offset by recycled content material. If we have a look at lithium, a mineral that’s not all the time recovered, the quantity recovered vastly impacts the p.c of demand that may be met with recovered lithium and the demand for newly mined minerals.
Our evaluation for lithium reveals how restoration charges dramatically affect future mining wants With recycling processes attaining a 90% lithium restoration charge, virtually 60% of lithium demand may be met with recycled content material in 2050, equaling virtually 5 hundred thousand metric tons from 2025 to 2030, or sufficient for 50 4 million common EVs[1]. Alternatively, decrease restoration charges improve mining necessities. A 50% restoration charge would require a further 200 and ten thousand metric tons of newly mined lithium in comparison with the usage of a 90% restoration charge. And a 25% restoration would require about 300 and forty metric tons extra newly mined lithium. Nevertheless, these would all be enhancements from the established order; at current, there is no such thing as a required restoration charge for recycling and, due to this fact, in lots of instances, no restoration of lithium.
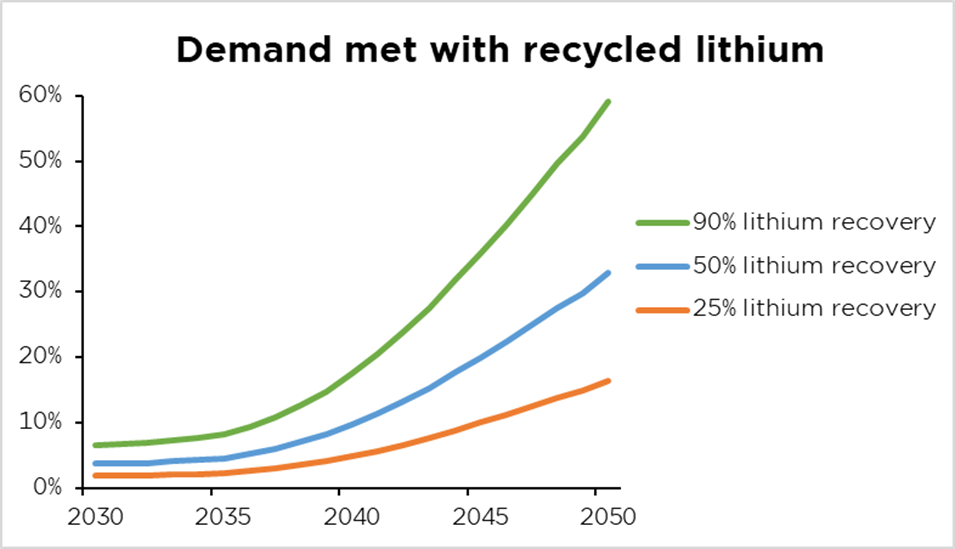
This calculation solely consists of US passenger car lithium demand and is predicated on the evaluation of Dunn et al. (2025). Extra restoration charges have been utilized to the Formidable Discount Technique to get these outcomes.
Mineral restoration is important to making a lower-impact and resilient provide chain
Mineral restoration charge necessities are a vital a part of making a secondary mineral provide chain and round economic system for lithium. Whereas mineral restoration charges haven’t but made it into battery recycling coverage in the USA, we will look to of us throughout the pond to discover ways to create and measure any such normal.
Appendix: How the EU wrote restoration charges into regulation
Together with restoration charges in battery recycling coverage doesn’t should be difficult. The EU legislative textual content beneath helps illustrate how different coverage makers may go about implementing restoration charges of their jurisdictions.
REGULATION (EU) 2023/1542 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL– mineral restoration charges for lithium-ion batteries
By 31 December 2027, all recycling shall obtain at the least the next targets for the restoration of supplies:
(a) 90 % for cobalt;
(b) 90 % for copper;
(c) 50 % for lithium;
(d) 90 % for nickel.
By 31 December 2031, all recycling shall obtain at the least the next targets for restoration of supplies:
(a) 95 % for cobalt;
(b) 95 % for copper;
(c) 80 % for lithium;
(d) 95 % for nickel.
Supplementing regulation – mineral restoration charge calculation and verification
[some language has been taken verbatim and has been modified to clarify and condense]
Enter fraction: the mass of waste batteries coming into the waste battery recycling course of, waste anode and cathode lively supplies, present collectors, and electrolyte salts. Recyclers shall decide the share of various waste battery chemistries current in an enter fraction by conducting a sorting evaluation of the fractions by steady or consultant sampling. This may be achieved utilizing one of many following strategies:
- on the premise of knowledge offered by the battery producers, the place that info is accessible on a label or in an digital file;
- by figuring out the chemical composition of all of the output fractions plus emissions and waste ensuing from remedy;
- by sampling and analyzing the enter fraction.
Intermediate fraction: the mass of waste batteries when it’s neither enter nor output fraction however destined for subsequent steps within the recycling course of which have the purpose of changing intermediate fractions into output fractions.
Output fraction: the mass of waste batteries obtained from the recycling course of derived from enter fractions and transformed into supplies, substances, or merchandise that may substitute main supplies, substances, or merchandise in industrial processes of producing. Metals similar to lithium contained within the slag aren’t taken under consideration in calculating the speed of restoration of supplies.
The mineral restoration charge shall be calculated on the premise of the chemical composition of the enter and output fractions utilizing the next equation:
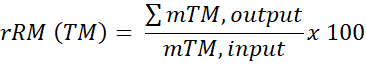
The place:
TM = the goal supplies; both lithium, nickel, cobalt, or copper
rRM = calculated charge of restoration of supplies from waste batteries in relation to a recycling course of [in mass %]
mTM, output = the mass of the goal materials in output fractions taken under consideration within the charge of restoration of supplies, specifically the mass of TM contained within the output fractions per calendar 12 months
mTM, enter = the mass of the goal materials within the enter fraction, specifically the yearly common mass of TM contained within the enter fractions per calendar 12 months
Extra necessities addressed by the regulation:
- The recovered materials shall have a TM content material as excessive as technically possible whereas avoiding extreme prices.
- In some instances, a number of recyclers could also be concerned on this course of that additionally course of intermediate fractions. The place a waste battery recycling course of is carried out at a couple of permitted facility, the primary recycler shall be chargeable for accumulating and offering the data required.
[1] Assuming an 80kWh battery and .11 kg/kWh of lithium















